Theory of Objective Motions - Einstein was wrong
Tiger Zhang, an independent scholar in Shanghai, China sent the following paper, which is the English version of a paper published in Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory, No.3, Volume 26, 2009.
The paper re-analyses Einstein's thought experiments on moving observers and comes to a quite different conclusion. The concept is that each planet, star and galaxy creates its own local medium body, and that those bodies or spheres of influence are separate but interact with each other. Those spheres of influence are real physical spaces with their own characteristics, not "inertial reference frames" as Einstein postulated.
This is the best analysis of those Einsteinian concepts on relative velocities I have seen, and so I would like to share it here.
From the conclusion of the paper:
"There is no perfect vacuum space in the universe. Medium consisting of particles always exists between the wave source and the receiver. The theory of relativity, based on the concept of perfect vacuum, is wrong and meaningless in physics."
- - -
Theory of Objective Motions of Wave Source and Receiver in Medium Body
Revised and English version written by Tiger Zhang, Shanghai, China, from Nov. 20th to 24th, 2015
Detailed and Chinese version published in Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory, No.3, Volume 26, 2009
1 Wave Sources and Receivers
Objects transmitting wave signals are wave sources, such as the sound sources of trains and the light sources of celestial bodies. People or objects receiving wave signals are receivers, such as the men listening to the sounds of trains and the telescopes in the outer space recording light signals from stars and galaxies. When we observe, we receive light signals from the light sources. All celestial bodies are wave sources and we are receivers of their wave signals.
2 Medium Bodies and Perfect Vacuum
Except perfect vacuum, which only exists in theory, not in reality, light transmits through medium, which consists of particles. When due to some external limitation, some particles are contained in a certain space, they form a material medium body. The external limitation can be a closed shell. For example, the shell of a train contains all the air in the train and forms the train's air medium body. The external limitation can also be a shapeless force. For example, the gravity of the earth limits the air around the earth and forms the earth's air medium body.
If a container is in a state of perfect vacuum, it makes a (perfect) vacuum medium body. There is no particle in a (perfect) vacuum medium body and it is a nonmaterial medium body.
Both material medium body and nonmaterial vacuum medium body are medium bodies.
3 Internal Independence and External Dependence of Medium Bodies
A small medium body may move in a large medium body. The large medium body is called the small medium body's mother medium body, and the small medium body is called the large medium body's son medium body. For example, the earth's air medium body is the train's air medium body's mother medium body, and the train's air medium body is the earth's air medium body's son medium body.
When receivers in a son medium body observe and measure wave sources in the son medium body, it is unnecessary to consider, and it is impossible to measure, the velocity of the son medium body in the mother medium body. This attribute of medium bodies is called the internal independence of medium bodies. Because of this attribute of internal independence,it is impossible to measure the velocity of a train in the earth's air medium body with sound, light, or electromagnetic wave experiments. It is also impossible to measure the velocity of the earth in the solar system with light or electromagnetic wave experiments. That is why Michelson-Morley experiment fails to detect the speed of earth moving around the sun.
When receivers in a son medium body observe and measure wave sources in its mother medium body, or when receivers in a mother medium body observe and measure wave sources in its son medium body, it is necessary to consider, and it is possible to measure, the velocity of the son medium body in the mother medium body. This attribute of medium bodies is called the external dependence of medium bodies. When we, the observers of the universe, receive light or electromagnetic wave signals from celestial bodies, and observe planets in the solar system, stars in the Milky Way, and galaxies outside the Milky Way, we must consider our motions as receivers in the solar system, in the Milky Way, and in the universe, as the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe are all material medium bodies.
4 Objective Durations and Subjective Durations of Wave Signals
Wave signals without durations, such as the light signal in Einstein's first paper of the theory of relativity, On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies, is unanalyzable and without value of analysis and measurement in physics. Period, frequency, and wavelength are all concepts based on the concept of duration. We use two observers' different judgements of a wave signal in a model of two trains to analyze quantitatively the Doppler effect of wave in a medium body and take the earth's air medium body as an example.
Let us assume a train S moves forward with speed VS in the earth's air medium body and there is an observer Sally in S. In front of S, another train R, moves forward with speed VR and there is an observer Robert in R. The speed of the wave in the earth's air medium body is V. At the moment of tS0, the front of a wave signal leaves S, and at this moment, the distance between R and S is dSR0. The front of the wave signal arrives at R at the moment of tR0. When the front of the wave signal propagates forward, R is moving forward too, so V(tR0-tS0)=dSR0+VR(tR0-tS0) and tR0=dSR0/(V-VR)+tS0. The end of the wave signal leaves S at the moment of tS1=tS0+τS, and the distance between R and S at this moment is dSR1=dSR0+VRτS-VSτS. The end of the wave signal arrives at R at the moment of tR1, so V(tR1-tS1)=dSR1+VR(tR1-tS1) and tR1=dSR1/(V-VR)+tS1. In Sally' s measurement, the signal starts at tS0 and ends at tS1, so Sally judges that the signal has duration of τS=tS1-tS0. In Robert's measurement, the signal starts at tR0 and ends at tR1, so Robert judges that the signal has duration of τRseeS=tR1-tR0=τS(V-VS)/(V-VR).
The duration of a wave signal measured by the observer moving with the wave source is defined as the objective duration of the wave signal. The duration of a wave signal measured by the observer not moving with the wave source is defined as the subjective duration of the wave signal.
5 Objective Characteristics and Subjective Characteristics of Wave Signals
Now assume the objective duration of the wave signal, τS, equals one objective period of the wave signal,TS, so we have τS=TS=1/fS and λS=V/fS, with fS and λS as the objective frequency and the objective wavelength of the wave signal.
The wave signal with one period cannot change to a wave signal with several periods, so in the measurement of receiver R, the wave signal still has one period, the subjective period, TRseeS=TS(V-VS)/(V-VR).
The ratio of the subjective period and the objective period is defined as y, so y=(V-VS)/(V-VR).
So, because of the motions of the wave source and the receiver, the subjective characteristics of the wave signal are: τRseeS=τSy, TRseeS=TSy, fRseeS=fS/y, and λRseeS=λSy.
Analysis above is suitable for sound signal when V is the speed of sound in the air. Analysis above is suitable for light signal and electromagnetic wave signal too when V is the speed of light in the air.
6 Theory of Objective Motions of Wave Source and Receiver in Medium Body
It is traditionally regarded that there must be a reference body (frame) to measure a body's velocity. But, in a medium body, the velocity of wave propagated from the wave source to the receiver, V, can and should be the standard of measurement for the velocities of the wave source and the receiver. So, in the measurement of the motions of wave sources and the receivers, the reference body is not needed. For convenience, in material medium body, the material medium can be regarded as the reference body.
The velocities of the wave source and the receiver in a medium body, VS and VR, measured using the velocity of wave propagated from the wave source to the receiver V as the standard of measurement, are defined as their objective velocities in the medium body.
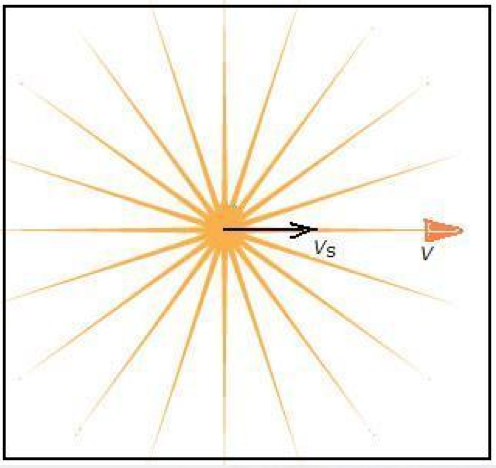
Figure 1:A Light Source Moving Objectively
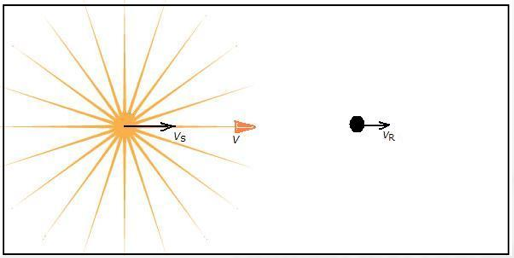
Figure 2:A Light Source and a Receiver Moving Objectively
When the directions of VS and VR are in the same line with the direction of V, y=(V-VS)/(V-VR). When the directions of VS and VR are not in the same line with the direction of V, y=(V-VScosαS)/(V-VRcosαR), whereαS is the angle between the vector VS and V and αR is the angle between the vector VR and V.
The theory considering the objective motions of the wave source and the receiver in medium body is called the theory of objective motions.
7 Shell Method of Velocity Measurement
A son medium body with a shell can measure its own velocity in its mother medium body without any reference body. Take a train as an example and assume the train move forward with speed VT. Set a wave source S and a receiver R on the top of the train outside the shell, with the wave source behind the receiver with distance dSR0. The front of a wave signal leaves S at the moment with speed V and arrives at R at the moment of tR0, so V(tR0-tS0)=dSR0+VR(tR0-tS0) and VT= V-dSR0/(tR0-tS0). In this way, the velocity of the son medium body in its mother medium body can be measured or verified.
8 Precise Radar Velocity Measurement
The airborne radar S transmits an electromagnetic wave signal with frequency fS to the target plane R. The target plane R reflects the signal. When the airborne radar S received the signal, the received frequency is fSseeR=fS[(V-VRcosαR)(V+VScosαS)]/[(V-VScosαS)(V+VRcosαR)]. Let r=fSseeR/fS, then the speed of the target plane can be calculated by
VR=[(1-r)V2+(1+r)VVScosαS)]/{[(1+r)V+(1-r)VScosαS)]cosαR}
If the radar is ground-based, then fSseeR=fS(V-VRcosαR)/(V+VRcosαR), so the speed of the target plane can be calculated by
VR=(1-r)V/[(1+r)cosαR]
9 Celestial Medium Bodies
Celestial medium Bodies are formed because of the gravity of the celestial bodies. The earth medium body includes the earth's air medium body, but it includes more. All the particles moving around the earth are in the earth medium body, regardless of their density, so the earth medium body goes as far as the moon, as the moon moves around the earth too. It does not look like a ball, but looks like a comet, as the medium is pushed by the solar wind.
The solar medium body is formed because of the gravity of the sun and it includes all the particles moving around the sun in the solar system. It starts from the surface of the sun and goes beyond Oort Cloud. All planets move around the sun near a plate. So are the particles. So the solar medium body does not look like a ball, but looks like an ellipsoid. The solar medium body is the mother medium body of the earth medium body.
The Milky Way medium body is formed because of the gravity of the Milky Way and it includes all the particles moving around the Milky Way. Like the solar medium body, it looks like an ellipsoid, but is much larger. The Milky Way medium body is the (1-level) mother medium body of the solar medium body, and the 2-level mother medium body of the earth medium body.
The universe medium body is the largest medium body. But is it the mother medium body of the Milky Way medium body, and the 2-level mother medium body of the solar medium body, and the 3-level mother medium body of the earth medium body? Up to now, we are not sure.
10 Reasons of the redshift
The earth moves in the solar medium body with velocity VEarth, and a wave source moves in the solar medium body with velocity VS, so in the observation, we have y1=(V1-VScosαS)/(V1-VEarthcosαEarth), whereV1 is the speed of the wave in the solar medium body.
The solar system moves in the Milky Way medium body with velocity VSolarSystem, and a wave source moves in the Milky Way medium body with velocity VS, so in the observation, y2=(V2-VScosαS)/(V2-VSolarSystemcosαSolarSystem), where V2 is the speed of the wave in the Milky Way medium body.
At the moment, let us assume the universe medium body is the mother medium body of the Milky Way medium body, and the Milky Way medium body moves in universe medium body with velocity VMilkyWay, and a wave source moves in the universe medium body with velocity VS, so in the observation, y3=(V3-VScosαS)/(V3-VMilkyWaycosαMilkyWay), where V3 is the speed of the wave in the universe medium body.
Redshift is defined as z=(λRseeS-λS)/λS, so z=y-1. So the redshift of the planets is from y1, the redshift of the stars is mostly from y2, and the redshift of the galaxies and quasars is mostly from y3. The reasons of the high redshifts of some quasars are the velocity of the Milky Way medium body in the universe medium body and the velocities of the quasars in the universe medium body, not the relative speed of the quasars leaving us.
11 Edge Convex Lens Characteristics of Celestial Medium Bodies
The density of the medium of a celestial medium body is not consistent. The nearer to the central celestial body, thedenser the medium becomes. The farther from the central celestial body, the thinner the medium becomes. When a celestial medium body exists between the wave source and the receiver, the wave has to travel past the medium in this celestial medium body and refracts. It looks like an edge convex lens existing between the wave source and the receiver. All phenomenon explained by gravitational lens can be explained with the edge convex lens characteristics of celestial medium bodies. When light from a star goes near the sun, it refracts because of the dense medium existing around the sun, not because of the gravity of the sun.
12 Space and Time
Another name of medium body, is medium space, or space. There is no perfect vacuum space in the universe. Medium consisting of particles always exists between the wave source and the receiver. The theory of relativity, based on the concept of perfect vacuum, is wrong and meaningless in physics.
Time is absolute and objective. Distance between the wave source and the receiver, and motions of the wave source and the receiver, cannot change time. The problem of simultaneity is caused by distance between the wave source and the receiver, not by motions of the wave source and the receiver as it is explained in the theory of relativity. The problem of duration is caused by motions of the wave source and the receiver, and the difference between the objective duration and subjective duration should be made clear using the theory of objective motions of the wave source and receiver in medium body.
Space and time are independent of each other, and they are not relevant. The word spacetime is meaningless in science.





I have to say I find this theory very difficult to believe, but this may be due to a lifetime of following Einstein. However, I have to say Einstein's Relativity makes perfect sense and has been confirmed by every test made of it. I feel this idea is just a cheap bid for fame. Fail.
OK so now what happens to the whole play of Gravity, Gravitons, Gravity waves...and so on ...is it to be replaced by the latent data within the locality body data defining its own environment ...sort of like we do with human laws? duuuuh?
Equating the gravitational force with the quantity or density of inert matter is incorrect. The correct interpretation of Kepler’s third law is: Gravitational force is equal to acceleration times the area: F = a . A. The weight of a body is equal to its mass times the acceleration: W = m . a. Weight is not Force. Please see my book GRAVITATIONAL FORCE OF THE SUN, my articles “New concepts in Gravitation” in PHYSICS ESSAYS, Volume18, (2005), pages 37–49, “Problems with the Gravitational Constant” in INFINITE ENERGY, Volume 10, No. 59, (2005), page 39, and http://parispolter.com/
Regards,
Pari Spolter
orbpublishing@msn.com
Biography of Dr. Pari Spolter is in Contemporary Authors, Volume 163.
The problem with both the mainstream view of relativity, and new ideas such as this, is that Einstein's eventual clarification of space, time, and what 'space-time' is has been missed. As I demonstrate in this essay:http://www.einsteins-revolution.com/EinsteinsAppendixV.pdf this holds the key to the unification of relativity, quantum mechanics and string theory.
I missed a space. The link to my essay is http://www.einsteins-revolution.com/EinsteinsAppendixV.pdf
Robert Fritzius says (by email):
Thanks for putting Tiger Zhang's article online. It ties in well with John G. Fox's 1965 extinction theorem.
Bob
Ar Juna (by email) says:
i just wanted to comment on the medium of space around a large heavenly body. I agree, something I postulated when the reports of the NASA experiments for transmission beyond Jupiter created distortions. The further away you are from a massive body like a star or planet, the less dense the local space. So we are talking like the magnetic field lines, as they grow weaker, but instead gravitational distortion lines not merely warping space convex and concave, but also compressing space, and quite possibly distorting time or magnetic fields.
In the interests of discussing this theory further, and reaching others who could help refine it, I am posting a letter from Tiger Zhang that gives more background...
First letter to my partner dissident scientists:
Can you accept the concept of medium space?
Tiger Zhang, written on Dec., 4th, 2015
1 Preface: What Am I Seeking for? The Answer is Truth and Partnership.
I write to you because you are in the Worldwide List of Dissident Scientists. After translating part of my first Chinese paper in 2009 into English, I sent it to Steven Bryan, (http://www.relativitychallenge.com/). He rightly found out the many mistakes of the theory of relativity and is waiting for his book, Disruptive: Rewriting the Rules of Physics, to be published. In his reply, he kindly suggested me to visit www.naturalphilosophy.org. And there I found the Worldwide List of Dissident Scientists. This is the way leading my correspondence to you.
From Nov. 23rd to Dec. 3rd, I wrote nearly 2,000 emails to you, one by one, man to man, to show my respect to you as a dissident scientist. But too much time sitting before the computer lets my eyes ache. I cannot do it again, so I thank you for all your replies and answer some of your questions here in this letter.
Nearly 10%, of the 2,000 dissident scientists, all with email address in the Worldwide List of Dissident Scientists, replied. Many offered kind advice and help. Nigel Cook pointed out some translation problems. So I corrected the mistakes and sent the paper rewritten to later scientists and to the vixra.org[1]. Lew Price said, “When it comes to gravity lensing or whatever you wish to call it, medium density may play a part. “ Sepp Hasslberger thought “it is the best explanation of Einstein’s concept of relative velocities I have read” and posted his comments and my paper on his blog at http://blog.hasslberger.com/2015/11/theory_of_objective_motions.html.(I am very glad that he posted it.) Russell Bagdoo said, “Your article provides a refreshingly point of view not only about motions of wave source and receiver in medium body but exposes the fact that no physicists can honestly say at the moment they truly understand space and time.” Alexander Chepick pointed out my mistake in z=(λRseeS-λS)/λS, and I am glad to accept his advice and correct my paper using his comment z=fS/fRseeS-1. Dr. Khan asked me, “If space is a medium how do massive objects move through this medium without any resistance?” I will answer this good question, “There is resistance.” And the detailed answer is in another paper[2]. Clark M. Thomas said, “You have elements of excellent insight.” Many others encouraged me in my endeavour.
What am I seeking for in the endeavor? Fame? No. I am seeking for the truth. I am just curious and want to find a reasonable answer to this question I found in my extensive reading in 2008: “Why does the light signal in the theory of relativity have no duration?” I was born in 1974 and my major in university is signal analysis. With years of working experience in signal analysis, I use the thinking way of signal analysis to analyze the light signal in the theory of relativity. To my surprise, it has no duration and cannot be analyzed. I think this is the key mistake in the theory of relativity and do more research. That is why I wrote my papers in Chinese and English. In fact, the Chinese version is much longer, but I have no time to translate all of my Chinese papers into English. I must find someone who can understand the brief English version first. That is why I correspond with you. I am seeking for partners in my search for the truth.
2 Space: Perfect Vacuum or Partial Vacuum?
Now the first question to my partner, you, is: Can you accept the concept of medium space? “VACUUM, theoretically, a space that contains no matter. No perfect vacuum is known to exist or has ever been made by man. Man can make a partial vacuum by removing most of the gas molecules from an airtight space.” These words are cited from page 1665 in The Golden Home and High School Encyclopedia, first printed in 1961. “Vaccum” in Wikipedia ( https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vacuum) tells us the similar information and more: “Outer space has very low density and pressure, and is the closest physical approximation of a perfect vacuum. But no vacuum is truly perfect, not even in interstellar space, where there are still a few hydrogen atoms per cubic meter.” So there is no perfect vacuum in reality, in the universe.
Then we come to the concept of medium space. The medium, consisting of particles around the solid, water, and air earth, moves with the earth, when the earth moves around the sun. It does not stay behind in the same place in the solar system when the earth moves away. So can we call it the earth medium body, or the earth medium space? The medium, consisting of particles around the sun and in the solar system, including the earth medium body, does not stay behind in the same place in the Milky Way when the Sun moves away. So can we call it the solar medium body, or the solar medium space? So, the Milky Way medium body is the Milky Way medium space? The universe medium body is the universe medium space? The reason is there is no perfect vacuum in the universe. Medium consisting of particles always exists between the wave source and the receiver. With the concept of medium consisting of particles, ether is not a necessary concept in science, is it?
[1] Theory of Objective Motions of Wave Source and Receiver in Medium Body, http://viXra.org/abs/1512.0034
[2] Resisting Force and Pushing Force of Medium in Motions of Celestial Bodies and Particles Moving at a Speed Greater than the Speed of Light, published in Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory, No.3, Volume 26, 2009.
Abstract: Planets move in solar wind and are influenced by resisting force and pushing force of the solar medium. The resisting force slows down the revolution speed of planets. The pushing force makes the planets move away from the sun and then makes their temperatures fall down in the long term. Pushing force of medium in the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe, is the cause of the expansion of the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Unless the particles collide with the medium, they can move at a speed greater than the speed of light as their motions are not influenced by the medium. Prove the particles in the cosmic radiation move at a speed greater than the speed of light.
http://tinyurl.com/pej2hyn
The theory of objective motions needs to be refined, as it is said by Sepp.
William suggested "A minor point for English readers; we would typically use daughter instead of son for progeny medium bodies, so mothers produce daughters and daughters are mothers of their daughters etc."
Rothwell said, "the naming of related characteristics as "mother" and "son" seems less than helpful, especially since it doesn't take much imagination to see the son as a mother with a son of his/her own, or even as a grandmother - or do I mean a grandfather?"
I accept their suggestion and will rename son medium body "daughter medium body".
How long does Eddington’s cigar last?
1 Eddington’s Cigar
In Eddington’s book in 1920, Space, Time, and Gravitation[1], in Chapter 1, he took his cigar’s duration as an example of Einstein’s time dilation:
Suppose “a man flies past us at the rate of 161,000 miles a second (VR=0.8656V)” ,so “the aviator is rapidly increasing his distance from us (VS=0) and the light-impressions take longer and longer to reach us.” “Suppose we both light similar cigars at the instant he passes us (tS0=0, dSR0=0). At the end of 30 minutes our cigar is finished. This signal, borne on the waves of light, hurried out at the rate of 186,000 miles a second (V) to overtake the aviator travelling at 161,000 miles a second, who has had 30 minutes start. It will take nearly 194 minutes to overtake him, giving a total time of 224 minutes after lighting the cigar.”
2 Common calculation of both the theory of relativity and the theory of objective motions:
VS=0, VR=0.8656V, V=186,000 miles a second.
tS0=0, dSR0=0, tR0=dSR0/(V-VR)+tS0=0.
tS1=30X60=1800 seconds (30 minutes) , τS=tS1-tS0=1800 seconds (30 minutes)
dSR1=161,000X30X60=289800000 miles,
tR1-tS1=dSR1/(V-VR)=11593 seconds (193.2 minutes, about 194 minutes as Eddington said),
tR1=dSR1/(V-VR)+tS1=13393 seconds (223.2 minutes, about 224 minutes as Eddington said),
τRseeS=tR1-tR0=13393 seconds (223.2 minutes, about 224 minutes as Eddington said).
3 Different calculations of the theory of relativity and the theory of objective motions
3.1 Time dilation calculation of the theory of relativity in modern physics books
VR/V=0.8656, (VR/V)2=0.75, 1/[1-(VR/V)]1/2=1/0.5=2.
So the ratio of time dilation is 2. So Sally’s cigar lasts 2X30=60 minutes.
In Eddington’s words, it is so:
“His watch like everything else about him (including his cigar) is going at half speed, so it records only 112 minutes elapsed when our signal arrives. The aviator knows, of course, that this is not the true time when our cigar was finished, and that he must correct for the time of transmission of the light signal. He sets himself this problem - that man has travelled away from me at 161,000 miles a second for an unknown time x minutes, he has then sent a signal which travel the same distance back at 186,000 miles a second; the total time is 112 minutes; problem, find x. Answer, x=60 minutes.”
(x+161,000x/186,000=112 minutes, so x=60 minutes.)
3.2 Calculation of the theory of objective motions
y=c/(V-VR)=7.44,
τS=τRseeS/y=13393/7.44=1800 seconds (30 minutes)
4 How long does Eddington’s cigar last?
In the theory of relativity, there is no difference between the motion of the wave source and the motion of the receiver on the receiving and observation result. This is only one velocity, the relative velocity, so in the example of Eddington’s cigar, the aviator sets himself this problem - that man on the ground has travelled away from him at 161,000 miles a second for an unknown time x minutes.
The theory of objective motions distinguishes the motion of the wave source from the motion of the receiver as they have different influences on the receiving and observation result. Our sound signal cannot overtake an aviator travelling at the speed of sound in the air medium, but we can receive sound signal from that aviator with its duration doubled, period doubled, and frequency halved. Our light or electromagnetic wave signal signal cannot overtake an aviator travelling at the speed of light in the air medium, but we can receive light or electromagnetic wave signal from that aviator with its duration doubled, period doubled, and frequency halved.
How long does Eddington’s cigar last? The theory of relativity cannot answer the question correctly. The theory of objective motions can.
5 How long does the aviator’s cigar last?
According to the theory of objective motions, the end of the light signal from the aviator’s cigar as the light source needs to cover the distance of dSR1 to reach the receiver standing on the ground, but does not need to overtake the receiver standing on the ground. So in this case,
VS=0, VR=0.8656V, V=186,000 miles a second,
tS0=0, dSR0=0, tR0=dSR0/V+tS0=0,
tS1=30X60=1800 seconds (30 minutes) , τS=tS1-tS0=1800 seconds (30 minutes),
dSR1=161,000X30X60=289800000 miles,
tR1-tS1=dSR1/V=289800000/186,000=1558 seconds (26 minutes),
tR1=dSR1/V+tS1=1558+1800=3358 seconds (56 minutes),
τRseeS=tR1-tR0=3358 seconds (56 minutes),
y=(V+VR)/V=1.8656,
τS=τRseeS/y=1800 seconds (30 minutes).
The calculation and data in this situation of the motionless observer and the moving light source are quite different from the situation of the moving observer and the motionless light source.
In the theory of relativity, the analysis of this situation is the same as it is in part 3.1 of this article, and there is no difference between the situation of the motionless observer and the moving light source and the situation of the moving observer and the motionless light source.
So, which theory is correct?
How do we measure time and what is time
Tiger Zhang, written on Dec, 24th ,2015 ,in Shanghai, China
Abstract: The meaning of time includes moments and durations. The problem of simultaneity (at the same moment or at different moments) is caused by distances, not by motions. The problem of duration is caused by motions. Distances and motions can cause the problems of simultaneity and duration, but cannot change time itself. Time itself is absolute and objective. Time can only be measured meaningfully using periods, and periods have durations.
1. How do we measure time?
Time is not an object or a space, which can be measured using length, area and volume. Time can only be measured meaningfully using periods. Without periods, how can we measure time? Is it possible to measure time without periods? I don’t think so.
A second is defined as the duration of 9 192 631 770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium 133 atom. A minute is defined as 60 seconds. An hour is defined as 60 minutes.
A day is defined as the period of the earth’s rotation. A month was first defined as the period of the moon’s revolution around the earth in the earliest civilizations. Later, the solar calendar was first invented by ancient Egyptians, and now, it becomes the international calendar. As a result, a month is not the period of the earth’s rotation now, but it is still about that period. A year is defined as the period of the earth’s revolution around the sun.
The period of the earth’s revolution around the sun, is neither an integer multiple of the period of the moon’s revolution around the earth, nor an integer multiple of the period of the earth’s rotation. So the duration of a year, is neither an integer multiple of the duration of a month, nor an integer multiple of the duration of a day. It brings troubles to the makers of the calendars. It also brings opportunities for the rise of astronomy, physics, and cosmology. Science grew up with the rise of astronomy and physics, with Copernicus and Newton as their representatives.
2 A century puzzled by Einstein in the meaning of time
In 1905, Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity brought the concept of space-time and brought a century puzzled by his theory in the connotation or meaning of time. In Einstein’s words, “two events which, viewed from a system of co-ordinates, are simultaneous, can no longer be looked upon as simultaneous events when envisaged from a system which is in motion relatively to that system.”[1] So, the problem of simultaneity is caused by motion, or different motions of different observers?
In Sir Arthur Eddington’s words, “Observers with different motions use different reckoning of space and time and that no one of these reckoning is more fundamental than another. Our problem is to construct a method of description of the world in which the indeterminateness of the space-time frame of reference is formally recognized.”
“Prior to Einstein’s researches no doubt was entertained that there existed a ‘true even-flowing time’ which was unique and universal. The moving observer, who adopts a time-reckoning different from the unique true time, must have been deluded into accepting a fictitious time with a fictitious space-reckoning modified to correspond......”
“the words time and space refer to one of the ‘fictitious’ time and space-primarily that adopted by an observer travelling with the earth, or with the sun-and our theory will deal directly with these space-time frames of reference, which are admittedly fictitious or, in the more usual phrase, relative to an observer with particular motion......”[2]
If you feel puzzed by these words, don’t worry. It is unnecessary to feel puzzled by these words, because these words, like those of Einstein’s, are quite deceptive. Even the “man most feared by the U. S. atomic bomb experts”, Nobel laureate for establishing quantum mechanics, Werner Heisenberg, was deceived: “In classical theory we assume that future and past are separated by an infinitely short time interval which we may call the present moment. In the theory of relativity we have learned that the situation is different: future and past was separated by a finite time interval the length of which depends on the distance from the observer. Any action can only be propagated by a velocity smaller than or equal to the velocity of light, Therefore, an observer can at a given instant neither know of nor influence any event at a distant point which takes lace between two characteristic times. The one time is the instant at which a light signal has to be given from the point of event in order to reach the observer at the instant of observation. The other time is the instant at which a light signal given by the observer at the instant of observation, reaches the point of the event. The whole finite time interval between these two instants may be said to belong to the ‘present time’ for the observer at the instant of observation. Any event taking place between the two characteristic times may be called ‘simultaneous’ with the act of observation.”[3]So, the problem of simultaneity is caused by distance: different distances of different observers?
3 What is time?
The meaning of time includes moments and durations. Time can only be measured meaningfully using periods. Periods have durations. Receivers (or observers as they are called in the theory of relativity) with different distances from the source of the same light signal receive the signal at different moments.The problem of simultaneity (At what moments do the signals start or the events begin? At the same moment or at different moments?) is caused by different distances, not by different motions. Receivers with different motions receive the same signal with different durations. The problem of duration (How long do the signals or the events last?) is caused by different motions, not by different distance. (Quantitative analysis is in the paper, Theory of Objective Motions of Wave Source and Receiver in Medium Body.[4])
Although there are problem of simultaneity caused by different distances and problem of duration caused by different motions, time itself cannot be changed because of distances and motions of the receivers and wave sources. Time itself is absolute and objective. A true even-flowing time, which is unique and universal, does exist. What is time? I cannot give it a definition. I can only give it its objectivity, which has been lost for a century.
[1]A. Einstein, On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies, 1905,http://www.fourmilab.ch/etexts/einstein/specrel/www/
[2]A. S. Eddington, The Mathematical Theory of Relativity, 1923, Chapter 1. Page 8
[3]W. Heisenberg, Physics and Philosophy: the Revolution in Modern Science. Great Books of the Western World, 1990, Volume 56. Page 423
4]Zhang Gui-Ping, Theory of Objective Motions of Wave Source and Receiver in Medium Body, Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory,26,692(2009), brief English version at http://vixra.org/abs/1512.0034.
The Origins of the Planets and their Later Developments
Tiger Zhang, written on Dec., 30 ,2015, as an answer to Dr. Vedat Shehu's mail this day
1. Why do planetary orbits follow Bode’s law? Because they were born out of the sun from its periodic explosions.
In my idea, the origins of the earth and other planets in the solar system are in the sun, as each planet was born out of the sun from its periodic explosions and every of the planets in the solar system was and is still in the solar medium body, which exists in the form of solar wind. So the cores of all planets have the same age of the sun because they were once parts of the sun, but the surfaces of all planets are much younger because they were formed later.
The planetary orbits follow Bode’s law, “first discovered by J. B. Titius in 1766 and brought to prominence by J. E. Bode in 1772.”[1] because each planet was born out of the sun from its periodic explosions. They follow Bode’s law since their birth, but they do not stay in their original orbits, because they were and are still pushed away from the sun by the pushing force of the solar wind, which may be neglected in the short term (though “short”, it can be as long as millions of years) but cannot be neglected in the long term (as long as billions of years). We know “the Sun yearly loses ~6.8X1019 g to the solar wind”[1], so in a duration of 0.1 billion years, the Sun loses ~6.8X1027 g to the solar wind, more than the mass of the earth (6X1027 g), without considering the daily mass loss of 1014-1016 g because of the Coronal Mass Ejections[1]. The pushing force of the solar wind is very strong near the sun, and it influences the perihelion motion of Mercury as the distance is only 0.3075 AU (4.60X107 km)[1], not as it is explained by the theory of relativity.
2. Why were there rivers on Mars? Because Mars was a warm planet billions of years ago.
Mars was warm and had rivers (as it is shown in the picture following) on its surface billions of years ago[1], but it was pushed away by the solar wind and became a cold planet. Earth is warm now but will become cold in billions of years. Venus is hot now but will become warm in billions of years.[2] The future of the human race is in Venus, not in Mars.
At the same time, the resisting force of the solar medium in the solar system slows the planets down in the long term, though it may be neglected in the short term, so the revolution speed of planets becomes smaller with the increase of the distance from the sun.
[1]Lucy-Ann McFadden, Paul Weissman, Torrence Johnson, Encyclopedia of the Solar System( Second Edition), 2007, which can be downloaded online. p.5, p.94, p.101, p.118, p.861.
[2]Gui-Ping Zhang, Resisting Force and Pushing Force of Medium in Motions of Celestial Bodies and Particles Moving at a Speed Greater than the Speed of Light, Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory, No.3, Volume 26, 2009.
If the velocity of a light wave is a constant velocity within the medium around Earth, the medium of particles must be fixed to the center of the Earth and fixed to the Earth's rotating surface. So, the medium must be rotating as Earth-centerred-Earth-fixed ECEF . This would explain the Michelson Morley null result and the GPS system.
But, in the text above, you say that the period of time does not change when distances and motions change. But, the time period of Cesium atom of 9 192 631 770 periods per second of time changes if the Cesium clock is raised to an altitude above sea-level, and the periods per second also changes if the clock velocity is not zero m/s to the ECEF. This was measured by Haefele and Keating. The experiment seemed to show that the true time was related to a frame that is non-rotating with the Earth, since the plane travelling Eastward had a negative time error of average Cs frequency, while the Westward travelling plane had a positive error, each compared to the ECEF stationary clock used as control. Are you saying that the time isn't affected, it is just that the Cs clock is in error due to the subjective motions of the S & R inside the Cs clock? i.e. Are you saying that the only clock that reads correctly in the ECEF rotating "medium" is the ECEF mounted clock?
Thank you for your information and idea, Weber.
First, I want to point out the wrong prediction of the theory of relativity. In "ON THE ELECTRODYNAMICS OF MOVING BODIES" (which can be download online), Einstein concluded that "a balance-clock at the equator must go more slowly, by a very small amount, than a precisely similar clock situated at one of the poles under otherwise identical conditions."
If we use the rotation speeds of clocks at the equator and at one of the poles (about 465 m/s and 0 m/s respectively), then the clock at the equator will be 3.8X10-8 s slower than the clock at the pole per year. And all clocks with different latitude and altitude will be different from each other, including the Cesium clocks in Paris, London, Beijing and those on the geostationary satellites. With the development of modern technology, these differences can be measured precisely. But there are no differences.
Second, I have heard about the experiments about clocks in planes flying eastward and westward. According to the information I have read in Chinese, there is no concluding proof in these experiments for or against the theory of relativity. Can the result of the eastward one with a negative time error and the westward one with a positive time error be explained by magnetic field, as mentioned by some people? I am not sure, because I have limited information and no research in these experiments.
I read https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hafele%E2%80%93Keating_experiment. But I am not sure about its meaning.
Do Cesium clocks staying in Paris, London, Beijing and those on the geostationary satellites show the differences predicted by the special theory and general theory of relativity?
Is the message in the wiki page true: "Nowadays both gravitational and velocity effects are, for example, routinely incorporated into the calculations used for the Global Positioning System." It is not consistent with your statement:" This would explain the Michelson Morley null result and the GPS system."
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hafele-Keating_experiment
Honestly speaking, I had no deep research in the general theory of relativity.
I have researched the special theory of relativity from 2008 and I am sure that Einstein's analysis of light signal from the source to the moving observer (receiver) is completely wrong.
According to the theory of relativity there are both kinematic time dilation and gravitational time dilation, and experiments about time dilation prove them to be correct, at least to the believers of the theory of relativity. I think further experiments about time dilation could not persuade them to disbelieve the theory of relativity. So I will focus my energy in radar velocity measurement. The atmosphere and the interplanetary medium can and should be the references of the motions of the source and the receiver in the velocity measurement of airborne radar and planetary radar. Who are familiar with radar or experts in radar? Who can help me?
Tiger:
I know that I am the last person to ask about SRT and GRT, since it has never been explained to me to the point where I understand the 2 theories. But, I am intrigued about your theory of objective motions and I would like to understand it fully. If your theory is correct, then it can be tested. But, you say that time is immutable and cannot be bent. If the test involves using Cs clocks, then we will need to determine if clocks have errors that need to be compensated for. If gravity can affect clocks, then we need to compensate. If the velocity of the clock relative to the distant stars in the Universe affects clocks, then this must also be compensated for. If time is immutable and only the clocks are getting a drift to them unrelated to "true" time, then we need to find the "true" time before we can test your theory.
I'll check on some contacts regarding GPS. I don't know of any radar experts. Can't guarranty who can help. But, whoever the expert is, we need to resolve how to correctly measure "true" time first, since velocity is distance divided by time. If you don't know "true" time, you can't measure velocity. The whole (V-Vs) and (V-Vr) calculation depends on measuring the 3 velocities. If all 3 clocks disagree, we need to compensate them to sync them up.
==
p.s. I just received a comment on the Hafele-Keating experiment from a collegue. He referred me to another paper here:
http://www.cartesio-episteme.net/H%26KPaper.htm
This author, Dr. A.G. Kelly , analyzed the data of the original paper and came to a totally different conclusion. His analysis was that the experiment had 4 clocks and 3 were unreliable for precision, because every time the plane landed to refuel, the 3 suspect clocks had high variance of drift for each leg of travel. So, he just looked at the one clock (i.e. clock#447) with tight variance of drift, and his conclusion based on this clock's drift is that the Eastward plane that had a very high velocity due to the added rotation of the Earth slowed clock#447 by 97 ns, and the Westward plane, that had a lower velocty relative to distant stars in the Universe due to it's travels mostly counter to the velocity vector of the Earth's surface rotation, had a speeding up of the clock by 27 ns. But, because there was only one clock, the experiment cannot draw any conclusions to any statistical confidence level. So, not only does the experiment not prove SRT, it doesn't disprove it either.
The experiment should probably be repeated, since there are clocks now that are 10 times more precise than the ones they used in 1979, and the experiment should use 20 clocks, and throw away the results for the outliers. There is now a clock that only costs $1500. So, a good experiment would be to put 20 clocks on a plane travelling Westward around the world, and a different set of 20 clocks on a Eastward plane travelling around the world at the same time. Then, when finished, keep all 40 at rest and measure the drift of the 40 for the same time span as the around the world trip. Th clocks would only cost ~$60,000. And the airlines would carry them in the cargo bay for minimal cost.
If it turns out that there is no kinematic time dilation (i.e. kinematic using the velocity vector relative to the distant matter in the Universe, or the velocity relative to the Earth's surface, or the velocity relative to the Sun), and only a gravitational time dilation (i.e. only a function of distance from sea-level) , this can be easily measured and compensated for any changes throughout the test if you wanted to test your theory.
I was thinking about a test and a good test would just be the exact train experiment that you referred to. Two high speed trains travelling toward each other, a laser, and a large number of Cs clocks on each train should be a good DOE.
Thank you for your interest in the theory of objective motions. If you really want to understand it fully, my suggestion to you is to read the maths, do the calculations, and draw the lines of the propagation of the wave from the moving source to the moving receiver. You can use air as the medium of propagation in the example of two trains (Section 4. Objective Durations and Subjective Durations of Wave Signals). In the other example of two planes (Section 8. Precise Radar Velocity Measurement),the quantitative calculation and drawing of propagation lines of the wave transmitting from the moving radar to the moving target and then reflected from the moving target to the moving radar, is critical in the analysis of the signal. I analyzed the signal for months in 2008 and at last concluded Einstein's analysis of the signal was completely wrong. Such analysis wasted no money. All you need to invest, is your time, patience and diligence.
And thank you for supplying Dr. A.G. Kelly's paper about the Hafele-Keating experiment. It said, "It(Hafele and Keating's paper in 1972) was published because it looked convincing and not because it gave a legitimate picture of the test results. To the unsuspecting reader, these graphs looked like proof of the success of the tests." I am glad to read it. But why did later experiments and papers mentioned in the https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hafele-Keating_experiment give unsuspecting readers "looked convincing" results? I am very surprised why so many people, experiments, and papers proved the correctness of the theory of relativity, because I am sure there is no mistake in my analysis of the signal from the source to the receiver. If anyone can find such mistake and point out it for me, I will feel very thankful to him. I will not be angry at all. But my conclusion at present is, Einstein's analysis of the signal was wrong.
Dear Weber, I am sure you are not the last person to ask about the theory of relativity. Many (or most?) people just follow Einstein's words and maths blindly because he is regarded as "the greatest scientist in the 20th century". They never go further to analyze the signal from the source to the observer (receiver): the leaving moment and arriving moment of the front of the signal, the leaving moment and arriving moment of the end of the signal, and these moments' effect on the durations, periods, and frequencies of the signal received by the receiver. They just pretend they understand the theory of relativity well. A few people doubt the theory of relativity. They find its mistakes, criticize it and write papers and books about it, but they do not analyze the signal too.
But to understand the theory of relativity, the signal should be analyzed, be quantitatively analyzed. I spent a few months analyzing it in 2008 and more time making my idea clear. Then I wrote my ideas down in Chinese and published the papers in 2009. I waited for responses from the scientific community in China for 6 years but there was none. So at the end of 2015, I wrote the theory of objective motions down in English and communicated with dissident scientists around the world. There are many positive responses and I think I have made a wise decision.
So I have spent years to reach you, Weber and other readers. I think the theory of objective motions deserves a little part of your time (a few minutes to read the words, a few hours to read the maths and do the calculations and draw the lines, and a few days and nights to understand its meaning fully). I am sure more and more people will begin to ask questions about the theory of relativity in 2016. Is it true? Is there time dilation? Is the theory of objective motions true? Is time itself absolute and objective? Do the motions of the light source and receiver change time itself? Or do they only change the characteristics of the light signal, not time itself?
Tiger:
Are you saying that you ran an experiment and measured the speed of light in the ECEF medium and determined that the speed of light is a constant to the ECEF medium? What is the 2008CY analysis that you refer to?
I's like to see the experimental proof of your theory.
If your objective medium theory is correct, and the ECEF son medium is the dominant effect on light speed,
there have been past experiments that show that the Earth son medium does not totally define the light wave speed.
Both the Michelson-Morley (M-M) and the Dayton-Miller (D-M) experiments showed that the speed of the wave depends
on the altitude. M-M near sea-level showed that the non-ECEF effect is ~ 1 km/s and the D-M at ~1700m showed that
the effect is ~10 km/s with the vector toward the constellation Draco.
Since the D-M effect was to siderial time, the dominant medium must be from the 230 km/s orbit of the mother medium
thru the grandmother medium of the Milky Way.
(i.e. the Earth's orbital velocity vector is only about 1/8th of the Sun's orbital velocity and it changes over a
year span, so it was probably indistinguishable from the instruments noise.
So, you should modify your theory to account for why the Grandmother' ~230 km/hr medium only affects the speed of
light at 1700 meters height to an amplitude of +/- 10 km/s.
Is this because most of the atmospheric particles at 1700 m altitude are ECEF and that the number of cosmic particles
(or particles ricocheting off of cosmic particles) is much lower that random speeds to the ECEF? If physical particles
cause the medium for light wave to travel in as you postulat, then you would think that the concentration of atoms in
the atmosphere that are moving in a net non-random direction toward Draco would be extremely low, since our Earth's
magnetic field keeps most of them away from the Earth's surface.
By the way, the plots showing the 10 km/s amplitude of light speed is here:
http://www.orgonelab.org/miller.htm
I would like to see the D-M experiment repeated in your country's city of Wenquan at 4870m altitude.
This is 2.9X higher than the Mt.Wilson D-M experiment.
If the results are, say, +/- 30 km/s effect, then it should be possible to calculate something about the nature
of the objective medium.
In any case, it would definitely support your objective medium theory (ver SRT) with a minor twist that the objective
son/mother/grandmother/g'grandmother medium's can somewhat blend.
The Structure of Earth Medium Body
The speed of light in the ECEF medium is not a constant, because the density of the medium changes with altitude. For convenience, the earth medium body can be divided into two parts.
The lower part of the earth medium body is the earth’s atmosphere, including the troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere, the thermosphere, and the exosphere. Planes fly in the troposphere and the stratosphere, so signals sent by airborne radar, reflected by target plane and received by the airborne radar, propagate in the atmosphere and in the earth medium body, not in perfect vacuum space. So at least, the concept of medium body is useful in Radar Velocity Measurement,as the Doppler effect here is determined by the motions of the radar and the target relative to the medium atmosphere, not by the motion of the target relative to the radar ,as it is suggested and applied now. Most satellites orbit the earth in the exosphere and in the earth medium body, not in perfect vacuum space. Though the density of the atmosphere “fall off exponentially with height”[1], the medium does exist.
The upper part of the earth medium body is the earth’s magnetosphere. Observed altitude of the magnetosphere, on the side facing the sun, is 70,000 kilometers.[2] On the other side, it is as far as where the gravity of the earth dominates, about millions of kilometers.
[1][2]Encyclopedia of the Solar System, 2nd Edition, p.172, P.523
By the way, I am still reading http://www.orgonelab.org/miller.htm, and need time to understand its meaning.
Experiment and natural scenes concerning the theory of objective motions
Tiger Zhang, written on Jan. 4, 2016, in Shanghai, China
As an independent researcher, I have to earn my living and invest my limited financial resource to books and other necessary tools. I have no resource to do expensive experiments, such as those suggested by Mr. Weber. But I did do an inexpensive experiment to prove the edge Convex Lens Characteristics of Celestial Medium Bodies (section 11) in the theory of objective motions. And natural scenes can show the Characteristics too.
The experiment needs a magnifier, a coin and a piece of paper. The magnifier is a solid medium body. Wave source and receiver cannot move in such a small solid medium body, so this experiment cannot show the difference between objective characteristics and subjective characteristics of light signals (durations, frequencies, wavelengths). But it can show the Edge Convex Lens Characteristics of Celestial Medium Bodies (section 11). Put the coin in the center of magnifier, let them face the sun, and put the piece of paper under them. When the sunshine passes this edge convex lens, colorful curves or rainbows will appear on the paper, depending on the distance from magnifier to the paper. If you turn the magnifier or move the coin, the curves or the rainbows on the paper will change. Even such a small medium body can reflect and disperse the light from the sun. Why cannot the huge medium bodies of galaxies do it? When a huge medium body of galaxy exists between the source (such as a quasar) and the receiver (such as Hubble Space Telescope), it reflects and disperses the light. I have some pictures showing the results of such reflection and dispersion, from an astronomy textbook in Chinese, though they were mistakenly explained as the results of gravitational lensing. Readers online can search such pictures with “gravitational lensing”, as it was so called now. There are differences between the Edge Convex Lens Characteristics of Celestial Medium Bodies and gravitational lensing.
A cloud between the sun and us can show the Edge Convex Lens Characteristics of Celestial Medium Bodies too, because the cloud is also an Edge Convex Lens. I have seen the Characteristics twice. The first was in April, 2010. I saw a circle-like rainbow shinning at the edge of the cloud. The second was in July, 2010. Colorful curves appeared at one corner of the cloud. But I did not have a digital camera or a smart phone, so I did not take photos. These colorful curves and rainbows are natural scenes showing the Edge Convex Lens Characteristics of Celestial Medium Bodies.
The structure of the solar medium body
The speed of light in the solar medium body is not a constant, because the density of the medium changes with its distance from the sun. For convenience, the solar medium body can be divided into two parts.
The lower part of the solar medium body is the sun’s atmosphere, including the chromosphere and the corona. The chromosphere is “the lowest part of the solar atmosphere, extending to an average height of ~2000 km” [1] from photosphere, the surface of the sun. The density of the chromosphere decreases logarithmically with distance from the center of the sun, from 10^17 particles/cm3 near the surface to 10^10 particles/cm3 at the outer boundary.[2] The corona is the outer atmosphere of the sun. The matter here is in the state of plasma, at the density of 10^9 particle/cm3, 10^−12 times as dense as the photosphere[3].
The upper part of the earth medium body is the heliosphere and the sun’s outer gravitational sphere of influence. In the heliosphere, the average density of particles (mainly protons) in the solar wind falls off with heliocentric distance (r, as r^-2), and is 3.0-20.0 particles/cm3 (5%-95% range) at 1 AU. On the side where the sun and heliosphere move closer “at a speed of ~23 km/s relative to the interstellar medium”[4], the heliocentric distance of the heliosphere is over 100 AU. One the other side, the distance is much larger.“On September 12, 2013, NASA announced that Voyager 1 had exited the heliosphere on August 25, 2012, when it measured a sudden increase in plasma density of about forty times.”[5] Outside the heliosphere, in the sun’s outer gravitational sphere of influence, the solar medium and the interstellar medium interact with each other and form a huge transitional sphere. Here, the particles from the solar wind and the particles from the interstellar medium slow down and at last deposit. That is why there is a sudden increase in plasma density of about forty times. The sun’s outer gravitational sphere of influence “extends out much farther to ~2×10^5 AU”[6]. The Kuiper belt, the scattered disk, and the Oort cloud are in the sun’s outer gravitational sphere of influence.
[1][4][6]Lucy-Ann McFadden, Paul Weissman, Torrence Johnson, Encyclopedia of the Solar System( Second Edition), 2007, which can be downloaded online. P.78,P.110-111,P.21,
[2]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromosphere,cited from Kontar, E. P.; Hannah, I. G.; Mackinnon, A. L. (2008), "Chromospheric magnetic field and density structure measurements using hard X-rays in a flaring coronal loop", Astronomy and Astrophysics 489 (3): L57, arXiv:0808.3334, Bibcode:2008A&A...489L..57K, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200810719
[3]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Corona
[5]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heliosphere
Internal independence of medium bodies
If there is no mistake in my comprehension of the Dayton-Miller experiment, the experiment is against the theory of objective motions, because it is against the internal independence of medium bodies.
Internal independence of medium bodies means when you are doing an experiment about waves in a train, with both the source and the receiver in the train , it is unnecessary to consider, and it is impossible to measure, the velocity of the train on the ground. Can you measure measure it?
Like the train medium body, the earth medium body and the solar medium body have its internal independence of medium bodies, too, though they are medium bodies without a shell. Here,the gravity of the celestial body (the earth or the sun) is the main factor forming the medium body, though the medium body is influenced by outside forces (solar wind or interstellar medium). With or without a shell, the principle is the same: you cannot measure, and it is unnecessary to consider, the daughter medium body' velocity in its mother medium body or grandmother medium body. So if your statement is true, ("Both the Michelson-Morley (M-M) and the Dayton-Miller (D-M) experiments showed that the speed of the wave depends on the altitude.") there must be some other factor or factors, such as the density of the medium, the motion of the medium, and so on.
Of course, outside its shell,it is easy to measure the velocity of the train on the ground. Standing on the top of the train, you can feel the strong wind: the motion of the mother medium body's medium relative to the daughter medium body. With Shell Method of Velocity Measurement (Section 7), it is also easy to measure the velocity of the train on the ground, with the sound source and the receiver on the top of the train, even when there is no relative motion between them. It is also possible to measure the velocity of the train on the ground, with the light source and the receiver on the top of the train, if we measure the leaving and arriving moments of light signals precisely. The reason is that both the light source and the receiver on the top of the train are in objective motions in the earth medium body.
Because the earth medium body and the solar medium body do not have a shell, to measure its velocity in their mother medium body is not as easy as it is in the case of the train medium body, but it is still possible. That is external dependence of medium bodies.
Sorry for my frankness, Weber. But I cannot compromise my beliefs to "account for why the Grandmother' ~230 km/hr medium only affects the speed of
light at 1700 meters height to an amplitude of +/- 10 km/s." I believe there must be other explanations.
Miller might be unfortunate because it seemed that his student Shankland betrayed him. Then it is story of power and struggle, not a story of science and truth. Facing the dominant theory of relativity, I sometimes feel it is impossible to win a place in the scientific community for the theory of objective motions. But there are such places when the theory of objective motions have practical values, such as the fields of sonar and radar. The new method to analyze Doppler effect, with the leaving and the arriving moments of the front and the end of the wave signal at its focus of analysis, has its own value. So, I am confident that I can win a place for theory of objective motions. As to the fate of the theory of relativity, I am not concerned.
Tiger:
There is a Wiki article regarding an experiment done by Fizeau, where he measured the speed of light in flowing water of velocity V and with an index of refraction n.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Velocity-addition_formula#Fizeau_experiment
Since the speed of light in still water medium (sub m) is Cm' = C/n, he expected to measure a speed of light in
flowing water medium of Cm = V + Cm' (the prime ' is the stationary medium). But, instead, what he measured was a speed of the light of Cm = ( V + Cm' ) / ( 1 + V * Cm'/c^2 ). So, the velocity of light is partially dragged along to a velocity higher than the speed of light, but not fully dragged to a summation velocity of (V + Cm'). So, by a measured experiment, the objective medium does not totally define the speed of light. It does so partially, but not totally.
So, I wonder about the effect of the n getting lower at higher altitudes. As the static particles in the Earth's atmosphere get more dilute, the effect of the grandmother medium of the MW galaxy may become more important.
Michelson did calculations and he measured +/-4 km/s that varied over sidereal time after he moved the interferomemter up to the top of a mountain. This means that the MW galaxy medium effects the speed of light and the higher up away from the Earth's surface, the greater the effect. He also calculated the direction of the apparent drift, and the axis roughly aligned with the Solar System's axis (i.e. perpendicular to the ecliptic; It must be that at the present time the Solar System's axis and the orbital vector align - maybe 50,000 years from now the axis and orbital vector will not align). So, by a quirck of our Solar System's orientation for this point in time in the MW orbit, there is little variation of light speed by season. But, because the Earth's axis is tilted by ~23 degrees, this means that the Earth daughter medium is moving through the grandmother MW medium such that over a sidereal time scale (i.e. 23.93 hrs period), the velocity of light varies.
But, what the Fizeau formula predicts is that if the MM experiment is moved to the city of Wenquan in China, the +/-4 km/s fluctuation in light-speed over the Earth's orbit of sidereal time change should increase, since the moving atmosphere has less drag higher up.
But, the question has already been answered about whether the speed of light is constant in all directions - it has been measured to fluctuate and the fluctuation frequency corresponds to the motion of the direction the Earth's rotational axis points toward the distant stars. So, the grandmother medium definitely has an effect on a light wave travelling within the Earth daughter medium.
Tiger:
I was re-reading your words regarding time, where you say on Dec 24, 2015; "1. How do we measure time? ... time can only be measured meaningfully using periods." I don't conceptually agree with this, since my natural inclination is to think of time as an absolute, such that events can be (& are) simultaneous in time.
For example, if a blind observer detects an event, like a lightening strike as one point in time, and another observer who has working eyes detects the same lightening strike at another time, nothing will ever convince me that the two different detections were not of a simultaneous event. The Occum's razor answer is that both observers must do some calculations to account
for the correct "absolute" time of the event because of the errors that can occur due to various factors, and after they back calculate the actual "absolute" time of their mutually perceived event, they both will agree that what they detected was actually an event (in this case the same event) that each perceived at a time later than the earlier simultaneous event (i.e. occurred at the same "absolute" time).
Every astronomer intuitively knows on every world between us and a supernova event, that the event that each world detects peaked in intensity at one absolute instant, and the closer alien on the closer world will see the peak first, and the further out worlds will see it later. There is probably no discussion by any of these aliens (except maybe on Earth) that the real time of the peak was not at an earlier absolute time that all aliens would agree with. There is a good write-up of the absolute time that the International GPS system uses here: http://www.ipgp.fr/~tarantola/Files/Professional/GPS/Neil_Ashby_Relativity_GPS.pdf
If you dig down through all of the words, and suspend judgement about the talk on relativity, the article is very instructive about how the GPS system finds the true absolute time system. This system basically synchronizes every ground based atomic clock worldwide and every satellite mounted clock using a coded digital signal transmitted to/& fro. Basically, the 1572.42 Hz signal radio wave is divided up into 1540 1's and 0's as a digital code that sends the satellite clock, identity and position data digitally and this data package is apparently refreshed every millisecond.
So, at any millisecond interval, all clocks are re-synchronized. Therefore, the only way that the integrated GPS system works that allows receivers on Earth to find coordinate location is 4 very important assumptions:
1. There is an absolute time (or a master clock if you will) that is used by the GPS system and it is the equivalent of the average of many atomic clocks located a hypothetically very far distance from the Earth's center (i.e. far away from Earth gravity effects on clocks) and these hypothetical clocks are fixed to the distant galaxies in rotation (i.e. called ECI for Earth centerred inertial)
2. The speed of light is a known constant for every transmitter and receiver in this Earth medium and is only constant to this ECI frame (that is, the ECEF frame is not used for the calculations of duration and speed {my previous comment was in error in that regard})
3. The Newtonian orbital parameters of the satellites can be calculated and broadcast by the satellites and thus exact x, y, z transmitter location in the ECI coordinate system can be calculated by the receivers for an absolute time for any transmitter
4. The system assumes all receivers can then back-calculate simultaneous events of radio signal occurance at an absolute instant of time for individual & known identity satellite transmitters and then use the intersection of the spherical radio wave light travel distances of 4 or more satellites to calculate the x, y, z location of the receiver.
So, basically, every millisecond, if I interpret this GPS article correctly, the GPS system of many receivers worldwide doing the same back-calculations are all proving that you theory of objective motions is correct.
You say, in the section "3. What is time?", that "The problem of simultaneity... is caused by different distances, not by different motions." So, I believe that the GPS system is using your assumption that light travels at a constant velocity of 299796 km/s in a medium that is ECI - i.e. centered only on the Earth for these satellites located 20,000 km up, and the medium is not rotating relative to the distant galaxies.
The implications of this seems to be that the objective medium that you describe for Earth, is not related to the Earth's surface or to the Earth's atmosphereic atoms, but this medium is fixed by the influence of distant galaxies. The most logical assumption is that the gravitational pull of the whole Universe may be fixing the medium, although another possibility is that photons from these distant galaxies may also be the fixing mechanism for the Earth medium.
And the GPS system is proving that simultaneous events can be programmed to occur by mankind at different locations and velocities using synchronized clocks to an absolute time.
Sir Eddington's words that "no one of these reckoning is more fundamental than another." is apparently incorrect, because the GPS system can only do calculations based on one reckoning here in the vicinity of Earth and in the Earth medium.
I'll do some more checking to see if there is any more experimental evidence.
Hi, Weber.
Thank you for your information about Fizeau and GPS. Neil Ashby's paper seems to prove the correctness of the theory of relativity. It is written deeply and with many details.
I am glad that you said
"...the GPS system of many receivers worldwide doing the same back-calculations are all proving that you theory of objective motions is correct." But I need some time to read and comprehend his paper. Can theory of objective motions be proved useful in GPS? At least we can try our best.
Tiger:
The Ashby paper starts with the assumption the the GRT and the SRT are correct. The trouble is that the assumption of both theories is that there is no absolute time. But, most of the paper involves showing how the GPS system has to first calculate what the absolute time is so that all of the clocks work and so the GPS system works. So, this tells me that there is a preferential clock system to use to enable all clocks to agree after an adjustment. Time is not relative then, and there is one true clock time and so we avoid the twin's paradox. If 2 twin's blast off in 2 rockets that move away from Earth in opposite directions at close to c speed, then turn around and return, then the simple answer is that both are younger than Earth citizen's, but the two twins are the same age, because each has moved thru the MW medium at the same speed. So, your theory of objective motions has no paradox. The time of the twin's hasn't slowed, it is just that the atom's of the twin's have slowed. The atom's of the Earth dwellers did not slow, because they are almost stationary in the medium that they were in.
There is another experiment that you should read. Here is a paper on the measurement of the speed of light to the Moon and back using a laserbeam:
http://arxiv.org/vc/arxiv/papers/0912/0912.3934v1.pdf#page=12
The data of interest to you is figure 3. This shows that the speed of light was constant for these measurements within the daughter Earth medium and it was measured as not constant in the mother Sun medium (i.e. fig 4). This matches your prediction exactly. Although the data would be better if it was taken over a full siderial month.
I'll keep looking for experimental evidence.
Hello, Weber.
I read Lunar Laser Ranging Test of the Invariance of c with a happy mood. Data in this paper proved “The observed speed of light measured by an observer moving at speed vO seems to follow the simple relation cO = c ± vO.” So the theory of relativity was proved wrong. And the theory of objective motions is correct.
Dear Weber, I am very glad that you comprehend the brief English version of Theory of Objective Motions completely. Mr Sepp Hasslberger and you are the first two men to understand and accept the theory of objective motions in the world. I think you can write a formal paper and submit it to one scientific periodical, as you read extensively and deeply and now own the new thinking tool of the theory of objective motions. In the near future, many parts of the scientific community, such as physics and astronomy, will feel the impact of the theory of objective motions, as it gives a new view and a new explanation to phenomena and experiments about time, space, motions, periods and frequencies. And we are making the impact now.
In the theory of objective motions, in the analysis of the light signal transmitting from the source to the receiver in medium body, inertial reference frames are not needed and are discarded, because they cause confusion, especially in the case of moving observer. In Section 5.2 (and 4.2 and 4.3) of Lunar Laser Ranging Test of the Invariance of c, there is such confusion too: does the distance change or does the speed of light vary, or both? In the theory of objective motions, there is no such confusion.
Tiger:
I am trying to get some clarification from the author of the article on lightspeed test by lunar laser ranging. So, I wouldn't draw any conclusions yet.
But, from your statements, I am unclear about what you predict using your theory. You said somewhere above that you believe that the speed of light is constant in the Earth medium and the Earth medium does not include the mother Sun medium. So, according to your theory, what do you predict will be the result of a measurement of the speed of light from the total round-trip duration (in s) of laser pulses sent to a fixed mirror on the Moon, and back, plus the known range to the Moon's retro-reflector from a transmitter/receiver on the Earth surface (i.e. distance in km known from the rotations and orbital parameters of the Earth and Moon about their common barycenter)?
Weber: I have tried to calculate VS and VR using data from Lunar Laser Ranging Test of the Invariance of c these three days, and find out that the velocities of the source (and the detector) and the retro-reflector (as one kind of receiver) cannot be calculated with those modeled distances and times-of-flight in Table 1. For example, when i=1000 and 1001, the calculated V+VS is about -210 km/s and the calculated V-VR is about 205 km/s (V is the speed of light in the medium), so both the calculated VS and VR are about the speed of light. It is impossible.
Only the series of observed time-of-flight are dependable data. But VS and VR cannot be calculate with them.
V(tR0-tS0)=dSR0+vR(tR0-tS0) , dSR0 is DL in the table.
V(tS2-tR0)+vS(tS2-tR0)=dRS0 , dRS0 is DB in the table.
So, (tS2-tS0)=dRS0/(V+VS)+dRS0/(V-VR), tS2-tS0 is observed time-of-flight in the table.
Using DL, DB and observed time-of-flight when i=1000, and i=1001, V+VS and V-VR are calculated. For convenience, c is used for V here.
Correction: For example, when i=1000 and 1001, the calculated V+VS is about -42 km/s and the calculated V-VR is about 205 km/s (V is the speed of light in the medium), so both the calculated VS and VR are about the speed of light. It is impossible.
I will do the calculation again and again. Are there some mistakes in my calculation?
There are some mistakes of calculation in the above replies at 3:06 PM and 5:48 PM on Jan 29, 2016: I did not calculate precisely enough, so V+VS varies from -42 to -210. I will check it later.
The principle is the same:
V(tR0-tS0)=dSR0+VR(tR0-tS0) , dSR0 is DL in the table.
V(tS2-tR0)+VS(tS2-tR0)=dRS0 , dRS0 is DB in the table.
So, (tS2-tS0)=dRS0/(V+VS)+dRS0/(V-VR), tS2-tS0 is observed time-of-flight in the table.
Using DL, DB and observed time-of-flight, such as in the cases of i=1000 and i=1001, V+VS and V-VR can be calculated.
Here is how I calculate (V+VS) and (V-VR) independently. The principle is the same:
V(tR0-tS0)=dSR0+VR(tR0-tS0) , dSR0 is DL in the table.
V(tS2-tR0)+VS(tS2-tR0)=dRS0 , dRS0 is DB in the table.
So, (tS2-tS0)=dRS0/(V+VS)+dRS0/(V-VR), tS2-tS0 is observed time-of-flight in the table ( data in the list of TLB nsec in the table. But instead of L(aunch)B(ouce), L(aunch)R(eceive) is the right subscript in this list, so TLR should be used and the data are from the list of TLB nsec in the table)
So TLR=DB/(V+VS)+DL/(V-VR). 1/(V+VS) and 1/(V-VR) are unknown. Two sets of TLR, DB, and DL should be used to calculate the unknown 1/(V+VS) and 1/(V-VR), such as the sets of i=1000 and j=1001.
Part one: the coming of the formula of (V+VS)
First,TLRi=DBi/(V+VS)+DLi/(V-VR).
TLRj=DBj/(V+VS)+DLj/(V-VR).
Second, TLRi-DBi/(V+VS)=DLi/(V-VR). (1)
TLRj-DBj/(V+VS)=DLj/(V-VR). (2)
Third, by(1)/(2), [TLRi-DBi/(V+VS)]/[TLRj-DBj/(V+VS)]=DLi/DLj.
Fourth, [TLRi(V+VS)-DBi]/[TLRj(V+VS)-DBj]=DLi/DLj=r.
Fifth, TLRi(V+VS)-DBi=rTLRj(V+VS)-rDBj.
Sixth, TLRi(V+VS)-rTLRj(V+VS)=DBi-rDBj.
Seventh,(V+VS)=(DBi-rDBj)/(TLRi-rTLRj)
Part two: the data to calculate (V+VS)
Now using the data (when i=1000 and j=1001), r=DLi/DLj=395234.670226/395234.629747=1.000000102417645
rDBj=1.000000102417645*395234.364378=395234.404857
DBi-rDBj=395234.404852-395234.404857=-0.000005
rTLRj=1.000000102417645*2.636719979756=2.636720249802
TLRi-rTLRj=2.636720274134-2.636720249802=0.000000024332
(V+VS)=(DBi-rDBj)/(TLRi-rTLRj)=-0.000005/0.000000024332=-205.490 km/s
Part three: the coming of the formula of (V-VR)
First,TLRi=DBi/(V+VS)+DLi/(V-VR).
TLRj=DBj/(V+VS)+DLj/(V-VR).
Second, TLRi-DLi/(V-VR)=DBi/(V+VS). (3)
TLRj-DLj/(V-VR)=DBj/(V+VS). (4)
Third, by(3)/(4), [TLRi-DLi/(V-VR)]/[TLRj-DLj/(V-VR)]=DBi/DBj.
Fourth, [TLRi(V-VR)-DLi]/[TLRj(V-VR)-DLj]=DBi/DBj=s.
Fifth, TLRi(V-VR)-DLi=sTLRj(V-VR)-sDLj.
Sixth, TLRi(V-VR)-sTLRj(V-VR)=DLi-sDLj.
Seventh,(V-VR)=(DLi-sDLj)/(TLRi-sTLRj)
Part four: the data to calculate (V-VR)
Now using the data (when i=1000 and j=1001), s=DBi/DBj=395234.404852/395234.364378=1.000000102405063
sDLj=1.000000102405063*395234.629747=395234.670221
DLi-sDLj=395234.670226-395234.670221=0.000005
sTLRj=1.000000102405063*2.636719979756=2.636720249769
TLRi-sTLRj=2.636720274134-2.636720249769=0.000000024365
(V-VR)=(DLi-sDLj)/(TLRi-sTLRj)=0.000005/0.000000024365=205.212
Part 5: Checking computations of (V-VR) with (V+VS)=-205.490 km/s from Part 2:
TLRi-DBi/(V+VS)=DLi/(V-VR). (1)
DBi/(V+VS)=-395234.404852/205.490=-1923.375370344056
TLRi-DBi/(V+VS)=2.636720274134+1923.375370344056=1926.012090618190
(V-VR)=DLi/[TLRi-DBi/(V+VS)]=395234.670226/1926.012090618190=205.209
Part 6: Checking computations of (V+VS) with (V-VR)=205.212 km/s from Part 4:
TLRi-DLi/(V-VR)=DBi/(V+VS). (3)
DLi/(V-VR)=395234.670226/205.212=1925.982253601153
TLRi-DLi/(V-VR)=2.636720274134-1925.982253601153=-1923.345533327019
(V+VS)=DBi/[TLRi-DLi/(V-VR)]=-395234.404852/1923.345533327019=-205.493
So,(V+VS) and (V-VR) are confirmed to be about -205 km/s and 205 km/s.
And it seems to me that there is no mistake in the calculations. As there is no problem in the observed time-of-flight TLR, the problem must exist in the modeled distances of DB and DL.
Tiger:
I have an Email to the author to explain the paper. I don't exactly know what frame O is. I think it may be ECI. but it may be fixed to the observer and fixed to the distant stars.
I also think that the formula of p13 top is incorrect, since it says: c = 2 * D_L / T_LR , so I asked about this too.
Since the bounce occurs at T_B, you need to know the x/y/z coordinates of the Moon mirror point at T_B and the Earth surface point x/y/z location at T_L and T_R. So, shouldn't the formula be: c = (D_LB + D_BR) / T_LR .
Here are the calculations I get: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1O1zeyn6dxoaKEjtLOSBH1ZXFYm6L6wuXhDCTNFdVTOA
It works out that the c is a constant and it is the same value for frame O and frame S. This tells me that the c speed is a constant in the Earth medium, which is (I think) what you predict. But, to really know for sure, more shots are needed over a sidereal month [this whole data-set happened within a scant 8 minutes!!), so the speed measured when the transmitter/receiver is travelling away from the Moon instead of toward and at different angles. And we need data 6 months later , when the mother medium influence is reversed. A series of shots during a lunar eclipse would be interesting too, since the D_LB plus D_BR will be longer distance than the D_L plus D_R [due to the transverse motion of Earth & Moon in the Sun medium.]. So, it should be that the two calculations (i.e. 2 different frames of Earth medium and Sun medium) give different lightspeed c values.
In Daniel Y. Gezari’s paper, frame O is the moving observer’s frame (section 4.2). In 4.2 and 4.3, he tried to make clear the meaning of frame O, and got cO = 2D/(T – ΔT)= c + vO. In this situation, when vo is moving (objectively) toward the source (vO>0) it is certain that cO>c and when vo is moving (objectively) away from the source (vO<0) it is certain that cO<c. In 5.2 he calculated the cO = 2DL/TLR and got a speed of light greater than c. But is the speed of light here greater than c? My answer is no. Here, the distance changes and the speed of light does not. His proof is the result of the theory of relative motions, including the theory of relativity. The moving observer’s frame causes confusion between the change of distance and the change of the speed of light.
In the theory of objective motions, when the observer or/and the receiver moves (objectively) in a medium body, the changing factor is distance, not the speed of light. And frames are not needed. So there is no confusion between the change of distance and the change of the speed of light.
If it can be done, on the opposite earth station of the Apache Point Observatory, a similar experiment will get a speed of light lower than c, because while the Apache Point Observatory is moving nearer to the moon, the opposite earth station is moving away from the moon. The distance always changes, but the speed of light does not.
Before doing the experiments, the two problems which should be solved are:
(1) The Bouncing Moment Problem: Can the bouncing moments be measured at the A15RR retro-reflector? If the answer is yes, then TLB and TBR can be measured precisely.
(2) The Distance Problem: How can the distances be measured or modeled precisely at the the moments of L(aunch) and B(ounce)?
If TLB and TBR can be measured precisely, and DL and DB can be measured or modeled precisely , then VS and VR can be calculated precisely.
In Table 1 of Daniel Y. Gezari’s paper, when i=1000, we have DLB/TLB=395264.274239/1.318459700008=299792.458=c, and DBR/TBR=395204.541726/1318260453789=299792.458=c, so TLB and TBR are completely calculated based on the modeled data of DLB and DBR.
So the exact bouncing moments, the distances ( DBs) of the source and the receiver at the exact bouncing moments, TLBs and TBRs are all calculated, not measured precisely. So they are useless to calculate VS and VR.
An simpler experiment to test the theory of objective motions
Here is a simpler experiment to test the theory of objective motions. The distance D between a ground station and a stationary satellite does not change, though there are the speed VS of the ground station and the speed VR of stationary satellite caused by the rotation of the earth. The light leaves the source of laser at a ground station at TL with the speed of light V and reaches the retro-reflector at the stationary satellite at TB. The light bounces and leaves the retro-reflector at TB with the speed of light V and reaches the detector at a ground station at TR. Do the speed VS of the ground station and the speed VR of stationary satellite caused by the rotation of the earth need to be considered here? Because of the internal independence of the earth medium body, the answer of the theory of objective motions to this question is no, so I make a bold prediction: D/(TB-TL)=V and D/(TR-TB)=V.
Unlike Daniel Y. Gezari’s experiment of laser between the earth and the moon, where distances and moments are difficult to be measured, in this simpler experiment, D, TL,TB and TR can be measured precisely without great difficulty.
In this simpler experiment to test the theory of objective motions, it is unnecessary to consider the changing density of the medium with height, and the earth medium can be regarded as a whole, and the speed of light in the earth medium can be regarded as V.
A simpler experiment to test the theory of objective motions